ankle lateral ligament tear test|lateral ankle ligaments stress test : export forward shift of more than 8 mm on a lateral radiograph is considered diagnostic for an ATFL tear WEBfutexcel.com.br. a) Para determinar a posição de cada clube na Fase de Grupos. clique e mova-os para cima e para baixo. b) Para avançar clique abaixo em: Fase Eliminatória. Simulador da Libertadores. Simule a .
{plog:ftitle_list}
webA equipe do site Giga Bicho acompanha ao vivo o sorteio da Mais Milionária 124. Ajude nosso site, na próxima vez basta digitar no Google Mais Milionária Giga Bicho para acessar nosso site. O resultado da Mais Milonária concurso 124 é publicado nesta página a partir das 20 horas de sábado do dia 24 de fevereiro de 2024.
An anterior drawer is done to test the integrity of the ATFL and CFL. With the ankle in plantarflexion, the heel is grasped with the tibia stabilised and drawn anteriorly. Talar tilt is done to assess the integrity of the ATFL and CFL .Objective Assessment: Assessment of ligamentous laxity: Swelling. Isometric ankle eversion/abduction. Chronic Ankle Instability Checklist. Following LAS, a comprehensive . Ankle Sprains are very common twisting injuries to the ankle that are the most common reason for missed athletic participation. Diagnosis can be made clinically with swelling and ecchymosis of the ankle and pain with range . forward shift of more than 8 mm on a lateral radiograph is considered diagnostic for an ATFL tear
First, have the patient lying down supine with the knee bent on the affected side. Then, observe the lateral aspect of the foot and ankle for hematomas or bruises. Then, locate the three lateral ligaments and palpate along their course for .For management purposes, ankle injuries can be considered under the following headings: • Mild to moderate lateral ligament complex sprain – treatable with early mobilisation and guided .
The 3 ligaments other than deltoid ligament is often referred to as lateral ligament. Interpretation: Positive if pain is reproduced in the area of syndesmosis. Maneuvers: External rotation test: Tibia is fixed with one hand .Mechanism of injury: Lateral ankle sprains usually occur when the foot rolls underneath the ankle or leg, also known as an inversion injury. bruising and difficulty bearing weight on the foot. .This protocol is intended to guide clinicians through non-operative management of lateral ankle sprain. This protocol is time based (dependent on tissue healing) as well as criterion based. . The management of common ankle sprains and the evaluation and management of high ankle sprains (syndesmosis injuries) are discussed separately. (See "Ankle sprain in adults: Management" and "Syndesmotic ankle injury (high ankle sprain)".) Other injuries of the lower leg, ankle, and foot are covered separately, including the following topics:
Anterior Drawer Test. Assesses: Anterior talofibular ligament (ATFL) Position: Knee joint in flexion and ankle in 10-15 degrees plantar flexion Maneuver: The examiner exerts a downward force on the tibia while .
lateral ligament sprain in ankle
Epidemiology. Lateral ankle sprains are the most common ankle injuries with an estimated incidence of 0.2% per year.About half of lateral ankle sprains are due to sports injuries, and they account for many athletic injuries 1-5.. The most common ankle injury is ankle sprain and of ankle sprains, a lateral ankle sprain is by far the most common, .Lateral ligaments: These start at the lateral malleolus (the end of the fibula, which forms the bump on the outside of the ankle). Then the three ligaments connect to the talus and calcaneus. . If your pain isn’t improving, your provider may order other imaging tests, such as MRI, to take pictures of the ankle ligaments. . Injuries to the .Adduction (varus) stress test. Purpose: The varus stress test shows a lateral joint line gap. Performance: A varus stress test is performed by stabilizing the femur and palpating the lateral joint line. The other hand provides a varus stress to the ankle. The test is performed at 0° and 20-30°, so the knee joint is in the closed packed position.Diagnosing Lateral Collateral Ligament (LCL) Tears Nonsurgical Treatment for LCL (Lateral Collateral Ligament) Tears . During a physical exam a doctor will perform specific assessments used to test for LCL tears. In addition to these tests, a doctor will check for any signs of trauma, such as swelling, bruising, and lacerations around the .
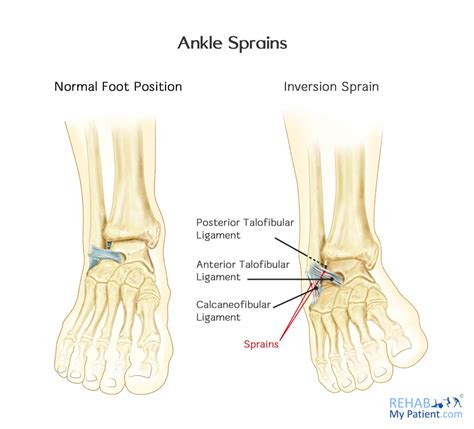
In the mildest presentations, the only structures to be injured are the lateral ankle ligaments, usually in the number or one or two. However, if the damage is more severe, we can observe lesions of all the lateral ligaments plus other structures like the talar dome, the base of 5 th metatarsal and the tibio-fibular syndesmosis.
deltoid ligament injury. loose bodies. Anatomy. See complete ligament of ankle . lateral ankle sprains are often able to bear weight. Physical exam . (Hopkin's) compression of tibia and fibula at midcalf level causes pain at syndesmosis. external rotation stress test. pain over syndesmosis is elicited with external rotation/dorsiflexion of .
The test is performed with the ankle held in neutral position while the talus is tilted into adduction and abduction. Repeat the test with the foot in plantar flexion to evaluate the integrity of the ATFL. A positive test result is 5° to 10° of increased inversion as compared with the non-injured ankle, indicating a CFL injury.
lateral ligament ankle injury
lateral ligament ankle anatomy
lateral ankle ligaments stress test
Tears to the lateral collateral ligament most often occur from a direct blow to the inside of the knee. This can stretch the ligaments on the outside of the near too far and may cause them to tear. This type of injury occurs in sports. Lateral collateral ligament tears do not heal as well as medial collateral ligament tears do. Severe tears may require surgery. In addition to acute injuries, pathology of the lateral ligaments of the ankle can lead to chronic lateral ankle instability, which is defined by persistent symptoms 1 year after primary injury [14•, 15•]. Up to 70% of patients who sustain an acute lateral ankle sprain can go on to develop chronic ankle instability [8•]. Following initial .
Studies show this is the most helpful test for assessing LCL injury. The test is performed with the examiner's hand stabilizing the femur and monitoring the lateral joint line while placing a varus force on the ankle. The test is first performed at 30°. Any lateral-compartment gaping is a positive indicator of LCL and potential PLC injury.
The CFL is injuries more commonly in dorsiflexion and inversion mechanisms. The posterior talofibular ligament is the least commonly injured of the lateral ligament complex. The medial deltoid ligament is the strongest of the ankle ligaments and tends to be injured with eversion injuries. Isolated deltoid ligament injuries are extremely rare.
A preoperative decisional tool for the anterior talofibular ligament repair in case of chronic lateral ankle instability. A routine inspection method of the ankle ligament in the case of the ankle ligament injury. A weight-bearing MRI is recommended because the transverse position and the coronal position can show the full length of the ligament.Lateral ankle ligament reconstruction is a surgical procedure to tighten and secure one or more ankle ligaments on the outside of your ankle. It typically takes place as an outpatient procedure. . an ankle sprain may stretch and .Introduction: Ankle sprains are one of the most common orthopedic injuries. Lateral ankle sprain refers to partial or complete tearing/disruption of the ankle ligaments on the outside of the ankle. Ligaments, in general, are the structures that connect bone-to .
In this test, the ankle is placed in dorsiflexion and the hindfoot is inverted. 33 Similar to the ADT, . Cao S, Wang C, Ma X, Wang X, Huang J, Zhang C. Imaging diagnosis for chronic lateral ankle ligament injury: a systemic review with meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2018;13(1):122.The ligament helps keep the outer side of your knee joint stable. A lateral collateral ligament (LCL) injury is usually caused by pressure or an injury that pushes the knee joint from the inside, which results in stress on the outside part of the joint. The symptoms of a tear in the lateral collateral ligament can include: Knee swelling The most common ankle injuries involve lateral ligament damage and are one of the most prevalent seen by physiotherapists. Approximately 7-10% of emergency department hospital admissions are due to ankle strains 1.The lateral ankle ligament is a complex of three different ligaments including the calcaneofibular ligament (CFL), anterior talofibular ligament .
The median prevalence for any lateral ankle ligament injury was 65% (36%-76% min-max) in the studies underdoing meta-analysis. Using this percentage as the pretest probability of injury for Fagan’s nomogram, a positive anterior drawer test (LR+ 3.97) increases the clinical likelihood of lateral ligamentous injury to 88%. . The accuracy of .
Sprained ankle — Injury to a ligament of the ankle can usually be treated with at-home care and appropriate exercises to get you back on your feet. . During an X-ray, a small amount of radiation passes through your body to produce images of the bones of the ankle. This test is good for ruling out bone fractures.Introduction. A lateral ankle sprain (LAS) is a frequently incurred musculoskeletal injury, with a high prevalence among the general population and individuals who participate in sports.1 2 About 40% of all traumatic ankle injuries occur during sports. For indoor sports, an incidence of 7 LAS per 1000 exposures has been reported.3 Despite the high prevalence and incidence of LAS .
feuchtigkeitsmessgerät beton laser
What are LCL tears? A lateral collateral ligament (LCL) tear is a knee injury that causes pain, swelling and bruising. Your LCL is a band of tissue located on the outside of your knee (the side that faces away from your body). This tissue connects your lower leg bones to your thigh bone. It stops your knee from bending outward abnormally.
The low ankle sprains don’t involve the high ankle ligaments. Low ankle sprains are what most of us think of when we hear someone has a sprained ankle. What ligaments are involved in a high ankle sprain? The ligaments that can be damaged or torn in a high ankle sprain include: The anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament: This is found in .Discover the essentials of Anterior Talofibular Ligament (ATFL) tears, a common ankle injury among athletes and active individuals. Understand symptoms, treatments, and recovery timelines to ensure effective healing. Learn about the R.I.C.E. method for immediate care, the importance of early diagnosis, and the role of physical therapy in rehabilitation. Prevent future sprains with . The ligament fibers stretched slightly or there is a very small tear. Your ankle will have minor swelling and tenderness to the touch. Grade 2 (Moderate). The ligament is torn, but it isn’t a complete tear. Your ankle has swelling over the injury and it hurts to move. Grade 3 (Severe). The ligament is torn completely.Pages in category "Ankle - Special Tests" The following 13 pages are in this category, out of 13 total. A. Anterior Drawer of the Ankle; E. Eversion Stress Test; F. Figure of Eight Method of Measuring Ankle Joint Swelling; I. Impingement sign ankle; K. .
feuchtigkeitsmessgerät beton obi
TV CANAIS - Veja vários canais de tv em seu celular ou pc. Assista tv online: GLOBO, RECORD, SBT E muito mais! Variedades. BBB 2024. Esportes. Premiere Canais. .
ankle lateral ligament tear test|lateral ankle ligaments stress test